Quantization Overview#
Quantization refers to the process of reducing the number of bits that represent a number. This process casts values from float type to an integer type that uses fewer bits.
How Quantization Works#
Linear quantization, also known as affine quantization, achieves this process by mapping the range of float values to a quantized range, such as the range for 8-bit integers [-127, 128], and interpolating linearly.
This mapping is expressed by the following mathematical equations:
# process of dequantizing weights:
w_unquantized = scale * (w_quantized - zero_point)
# process of quantizing weights:
w_quantized = clip(round(w_unquantized/scale) + zero_point)
In the above equations, w_unquantized and scale are of type float, and w_quantized and zero_point (also called quantization bias, or offset) are of the quantized data type.
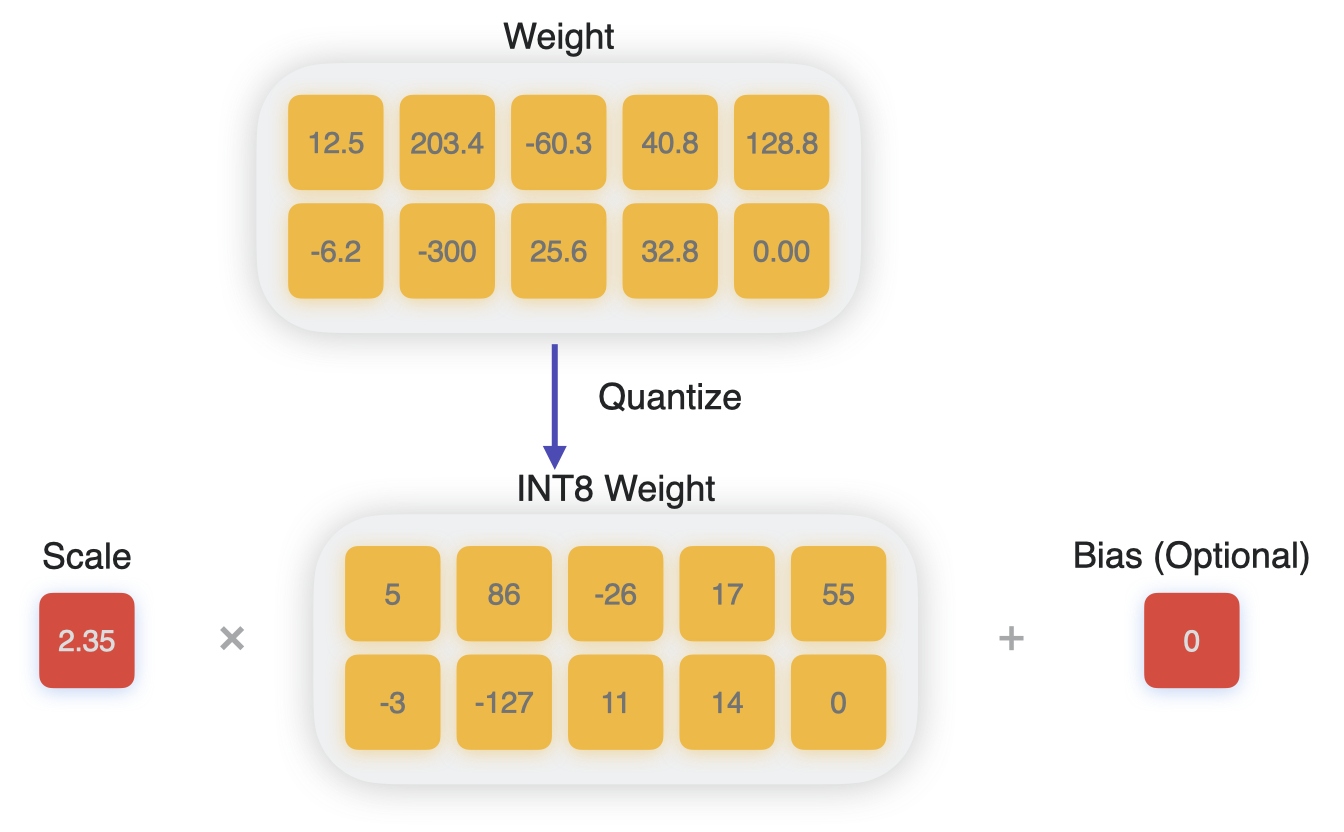
Process of quantizing to int8.#
Quantization precision#
For quantizating weights, 8-bit as well as 4-bit precision is supported. For activation quantizations, 8-bit is supported.
Symmetric Quantization#
When quantization is performed, constraining the zero_point to be zero is referred to as symmetric quantization. In this case, the quantization and dequantization operations are further simplified. This is the default mode used by Core ML Tools.
Quantization Granularity#
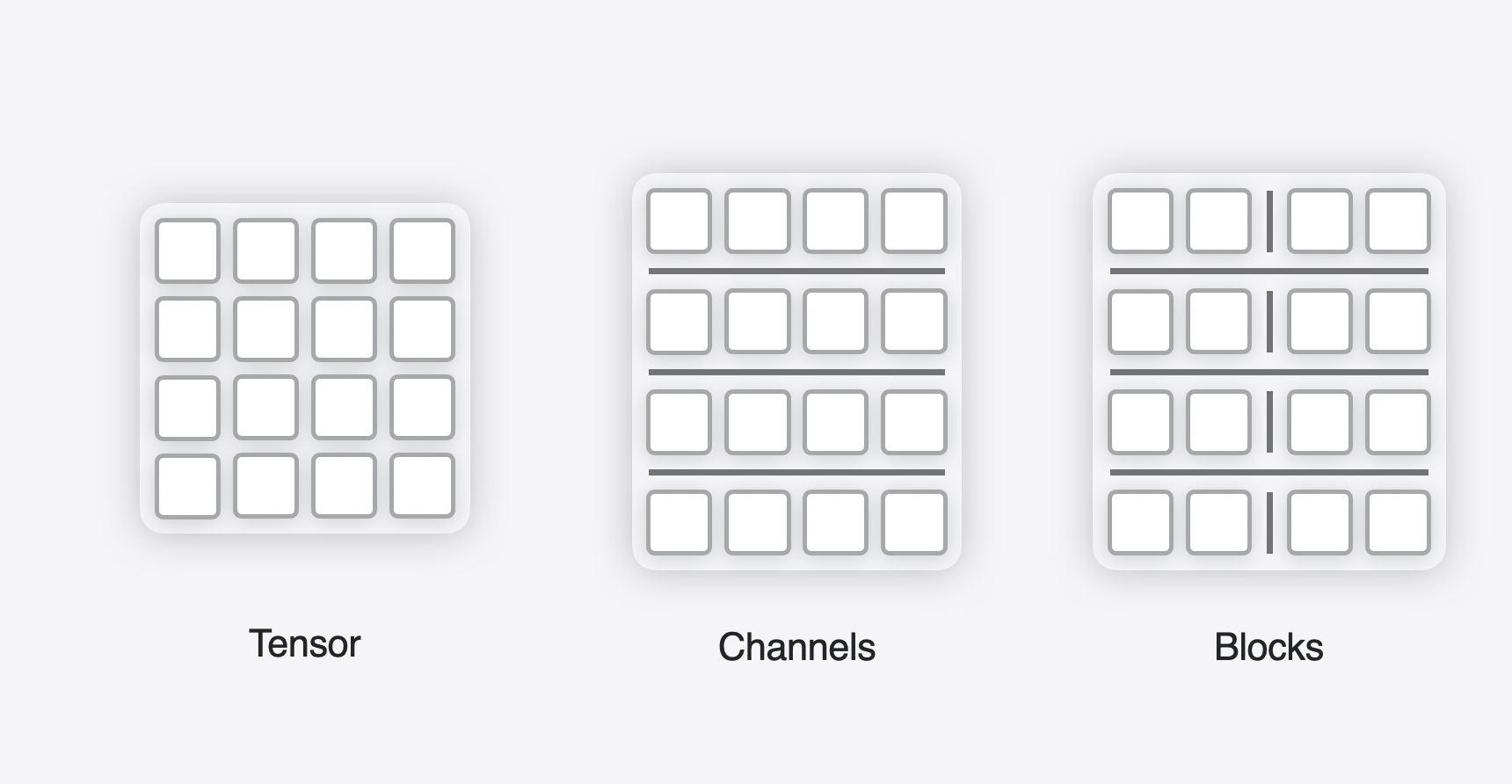
Different granularities supported for quantization.#
There are three modes supported for QuantizationGranularity: per_tensor, per_channel, per_block. per_tensor granularity computes a single float scale value (and zero point, in the case of symmetric quantization) for the whole tensor. per_channel granularity uses a scale factor for each outer dimension (also referred to as the output channel) of the weight tensor. The per_block granularity shares scale factors across blocks of values in the weight tensor. This helps provide more fine-grained control when quantizing the weight values, which helps improve the accuracy of the model.
Activation Quantization#
Unlike the Pruning or Palettization compression schemes that compress only weights, for 8-bit quantization, activations of the network can also be quantized with their own scale factors.
Activations are quantized using per-tensor mode. During the process of training or passing calibration data through the model, the values of intermediate activations are observed, and their max and min values are used to compute the quantization scales, which are stored during inference. Quantizing the intermediate tensors may help in inference of networks that are bottlenecked by memory bandwidth due to large activations.
On newer hardware with A17 Pro or M4 chips, such as the iPhone 15 Pro, quantizing both activations and weight to int8 can leverage optimized compute on the Neural Engine. This can help improve runtime latency in compute-bound models.